This entry is also available in: Russian Chinese (Traditional)
The year 1941, the last year of peace… We got only six months of that, and the USA got almost the entire year. Only after the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7th, 1941, the US entered the Second World War. During eleven months of the year 1941, the Americans were engaged in other ‘battles’: on the baseball field between New York Yankees and Brooklyn Dodgers, and at the local motorcycle market between Harley-Davidson and Indian. No less effect than the New York Yankees’ in the World Series, produced the appearance of a 48 hp Harley-Davidson FL – one of the most powerful motorcycles in the world at that time.
The battle of two giants of the U.S. motorcycle market, the Harley-Davidson and Indian, which took the first half of the twentieth century, was epic indeed. At first, the firm from Milwaukee completely lost to rival from Springfield (before World War I, sales of its motorcycles were two to three times lower), and if the Harley-Davidson won in the end, it was a painfully difficult victory on points. The two rivals watched each other closely immediately responding to each strike. In the 1920s, this led to their production programs almost mirroring each other: the 1,206 cc Indian Big Chief corresponded to the 1,207 cc Harley-Davidson JD, the 998 cc Indian Chief corresponded to the 989 cc Harley-Davidson J, and the single-cylinder 348 cc Indian Prince corresponded to the single-cylinder 346 cc Harley-Davidson А.

Harley Davidson EL from the «Motorworld by V.Sheynov» collection
In 1927, the Indian company management made a strong move: they bought the Ace company, which produced four-cylinder bikes designed by the famous engineer William Henderson. The Harley-Davidson company made an equal response: instead of developing its own four-cylinder engine, they put all efforts into the development of an ohv V-twin, which would not be inferior to the to Indian Four in dynamics, but at the same time would be cheaper in production. In 1936, the E Series entered the market, with 989 cc engines rated at 37 hp (basic E model) or 40 hp (boosted engine EL model). The Harley-Davidson EL was able to accelerate to a speed of 100 mph (160.9 km/h). No bike, except the EL, could offer such power for such price ($380). The market appreciated the innovative ohv model, which earned the nickname ‘Knucklehead’ because of the appearance of valve caps. Knuckleheads, despite the flaws (oil drips and breakage of valve springs), became bestsellers.
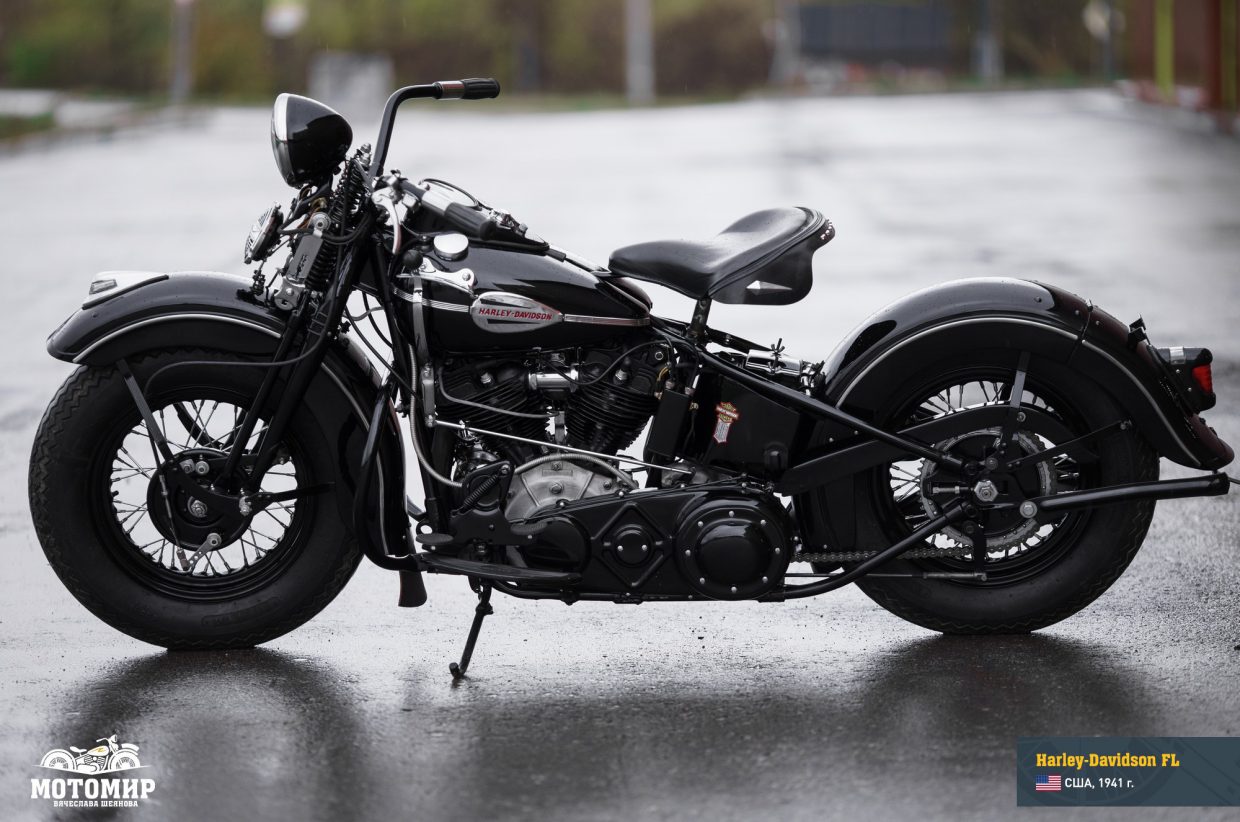
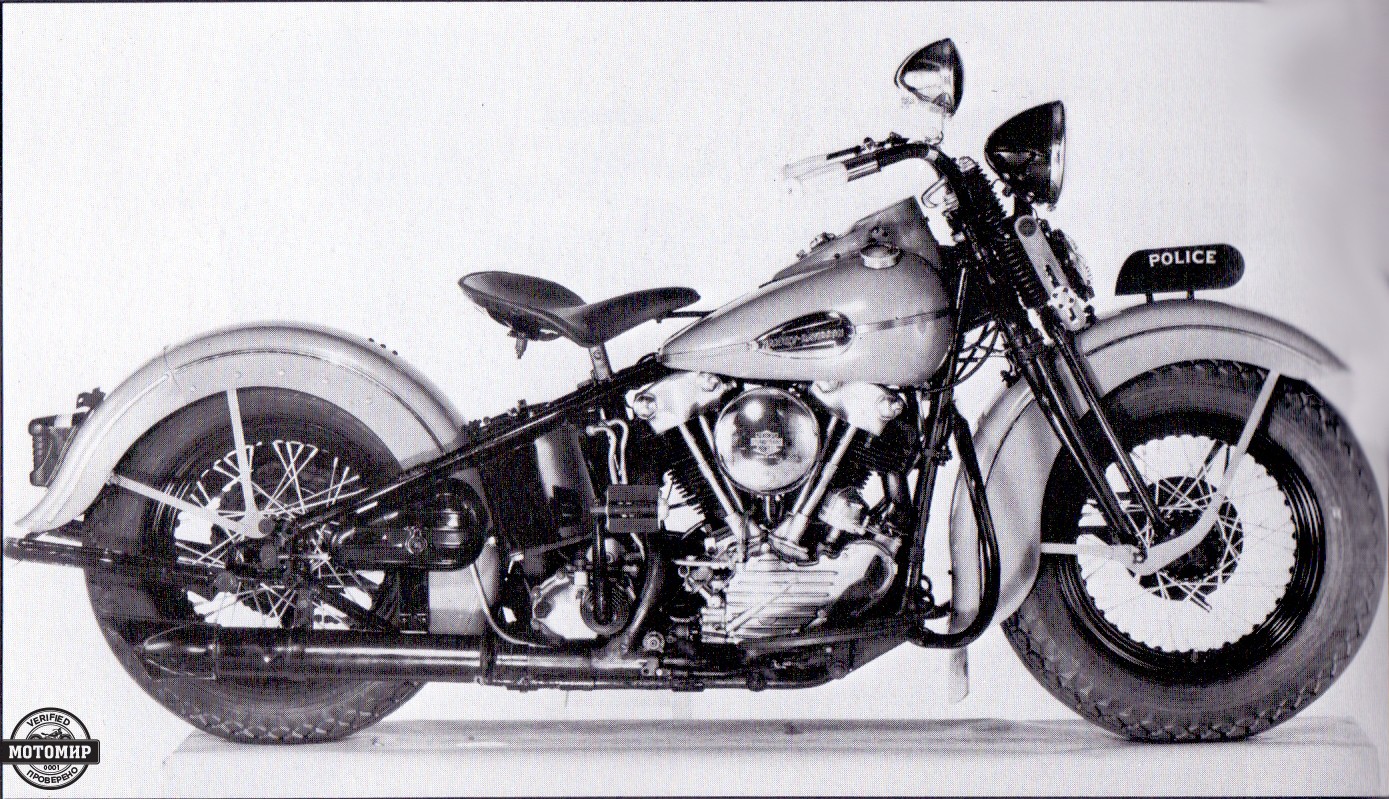
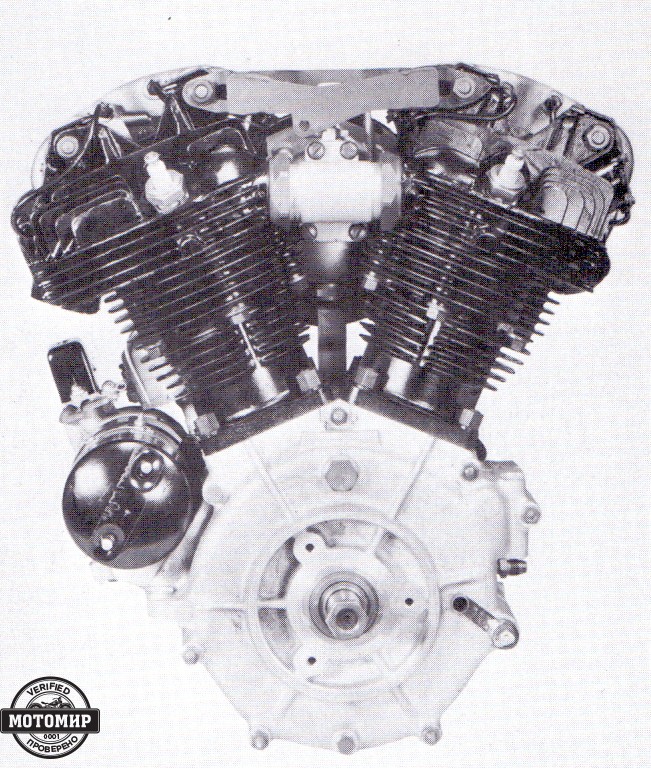
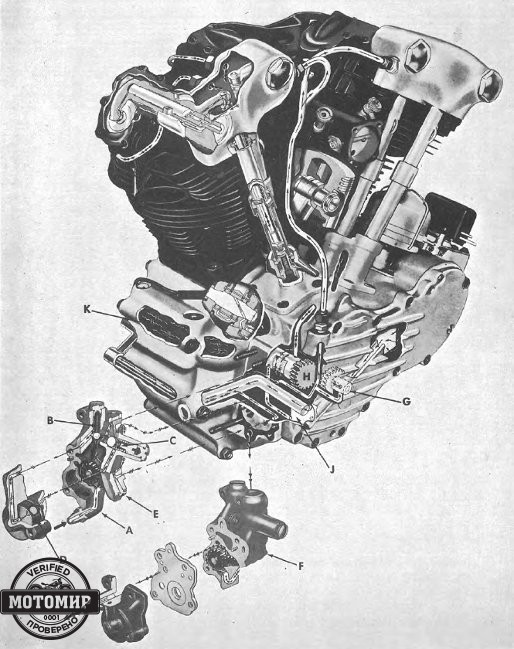
Both ordinary bikers and police departments gladly bought the E model. However, in the country of highways and cheap eight-cylinder cars even such dynamics were not enough. Therefore, by the 1941 season, at the request of special services was developed an ohv motorcycle with an increased capacity. It got the FL index and was equipped with a 1,207 cc engine. This engine developed 48 hp at 5,000 rpm, which provided excellent acceleration, while a declared top speed of 95 mph (153 km/h) was lower, compared to the EL model. The main features of FL were the same as every E-series machine had; cylinders and cylinder heads made of cast iron, assembled crankshaft with roller bearings, overhead-valve drive via pushrods from the single camshaft, dry sump lubrication system with an oil tank located under the seat. The traditional design feature of the Harley-Davidson engine was the forked connecting rods with integral lower heads. This design allowed the cylinder axles to be placed in one plane, which reduced the width of the engine, the load on the main bearing, and vibrations. On the other hand, the rear cylinder was completely shaded by the front one, which deteriorated its cooling.
The increased in working volume was due to both the cylinder diameter (from 84.24 to 87.3 mm) and stroke (from 88.9 to 100.8 mm). The Linkert carburettor also provided increased power, with its cone diameter increasing from 28.5 to 33.3 mm compared to the EL model. The increased torque was due to the new crankcase design. The reinforced crankshaft was almost 2 kg heavier than before. The redesigned rocker arms allowed for better lubrication of the gas distribution mechanism.
The torque from the motor was transmitted by a double chain to a four-speed manual gearbox installed in a separate unit. The newly developed multiple-disc clutch had a 65% larger lining area. The chassis was based on a powerful duplex tubular frame. The bike was equipped with a Springer fork and the rigid rear suspension was compensated by a spring seat. The Springer fork was so good that the license for it was acquired by the manufacturer of “two-wheeled Rolls-Royce”, British company Brough Superior; Harley-Davidson used it on vintage models and in the XXI century. Because of this saddles, the Harley-Davidson company prolonged with the introduction of soft rear suspension until 1957. Comfort was also facilitated by the transition to standard tires 5.00-16 instead of previously used 4.50-18.
Harley-Davidson bikes are considered excellent examples of the art deco style, so popular between the world wars, and the FL model was no exception. A drop-shaped gas tank and elegant fenders made the appearance dynamic. A metallic stripe running over the fuel tank merged into the diagonal frame element. A huge speedometer flanked by control lamps stood out on the dashboard. The lux version of a bike had a chrome-plated dashboard. The new silencer had a rocket-like end (instead of the old ‘fishtail’), which decreased the noise level and made a better appearance.
Except for three-wheeled Servicar, the Harley-Davidson FL became the most expensive model in the production program in 1941 – the price was $465, which is $40 more compared to the EL model). Let’s have a look at some figures for better understanding: the annual average income of an American was $515; the cheapest Ford cost $684. Nevertheless, only the WL model outsold the FL. The total number of FLs sold was 2,452, which is 172 units more compared to the EL. But on December 7th, 1941, the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, and the USA entered the WWII. The FL model was not included in the military’s list of orders, so its production has been frozen at the miserable level (for example, only 33 machines were manufactured in 1943). However, after the victory, it was back in the game again: 3,986 FLs were sold in 1946 (only WL model outsold FL).
In 1948, the Knuckleheads were replaced by the upgraded Panheads, which had hydraulic pushrods and cylinder heads made of lightweight alloy. But the “FL” index has survived to this day – it is present in the factory designation of the Harley’s Road King, which is considered a direct descendant of the 1941 Harley-Davidson FL.
From 1941 to 1947, a total of 14,954 FL motorcycles were produced, as well as several hundred of the F model, with reduced compression.
| Manufacturer | Harley-Davidson Motors Co., Milwakee (Wisconsin, USA) |
| Years of manufacture | 1941-1947 |
| Quantity produced, units | 14 954 |
| Price | 465 $ |
| Today’s value | N/A |
| ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION | |
| Type | V-twin, OHV |
| Engine capacity, cc | 1207 |
| Bore and stroke, mm | 87,3 х 100,8 |
| Engine rating | 48 hp at 5000 rpm |
| Sparking | Battery type |
| Carburetor | Linkert |
| Battery | 6 V |
| Clutch | Multiple-plate, dry |
| Transmission | 4-speed |
| FRAME AND WHEELBASE | |
| Frame type | Tubular, duplex |
| Front suspension | Springer, with frictional damper |
| Rear suspension | Rigid |
| Brakes | Drum type |
| Wheel size | 5,00 x 16 |
| DIMENSIONS | |
| Length, mm | 2300* |
| Width, mm | 1020* |
| Height, mm | 1130* |
| Wheelbase, mm | 1510* |
| Ground clearance, mm | 115* |
| Seat height, mm | 800* |
| Mass, kg |
261
|
| Gas tank size, l | N/A |
| Maximum speed, km/h |
153
|
| Range, km | N/A |
Thanks to the team of Harley-Davidson Russia and CIS for the provided archive photos.