This entry is also available in: Russian Chinese (Traditional)
Motorworld’s newspaper №59
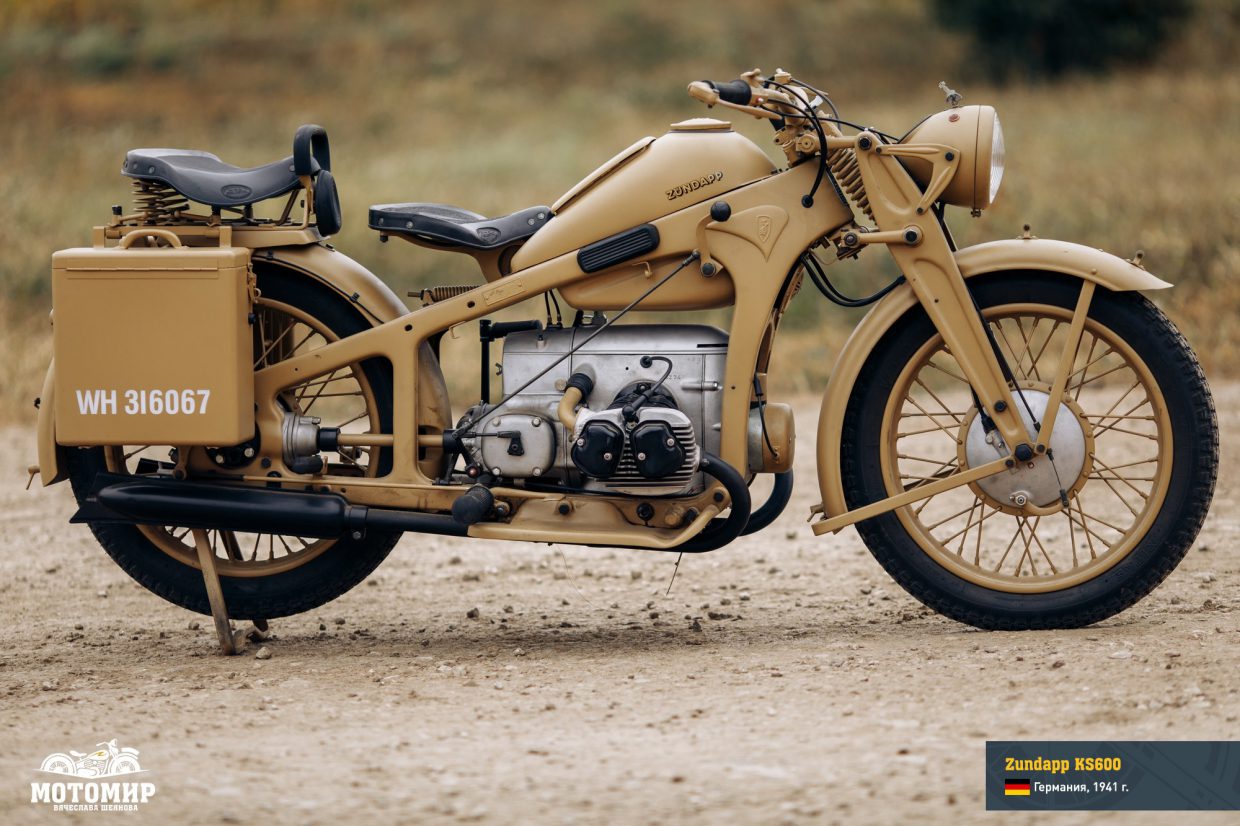
The Zündapp motorcycle plant was founded in 1917 for the manufacturing of military equipment (Zünder und Apparatebau GmbH stands for Detonators & instruments Company). Twenty years later, most of its products were supplied to the Wehrmacht. Despite the fact that Zündapp KS600 bikes were extensively advertised as civilian motorcycles (as evidenced by the branded brochures), the vast majority of them went to the Army and police.
TThe first Zündapp motorcycles (the K series) designed by Richard Küchen were introduced in 1933 at the Berlin Show. The K series consisted of six models having different engines, from a one-cylinder two-stroke engine to a four-cylinder four-stroke one, but all engines shared the same feature – these were rear-driven bikes (a drive shaft was used), which had a unified chassis and a frame made of pressed elements. At first, four-stroke engines were the flathead ones. Then, in 1936, an overhead valve engine having 500 cc displacement appeared, which was installed on the KS500 model. The engine could accelerate a bike to a speed of 130 km/h at 26 hp, which was comparable to a bike equipped with a 800 cc engine. It was powerful but badly suited for a sidecar. For this reason, the company introduced a compromise option – Zündapp KS600. The engine displacement was increased to 596 cc, the number of carburetors was decreased from two to one – this resulted in increased engine power at low RPMs and the capacity at high RPMs increased to 28 hp. Also, it had a stronger chassis to smoothly operate with a sidecar.
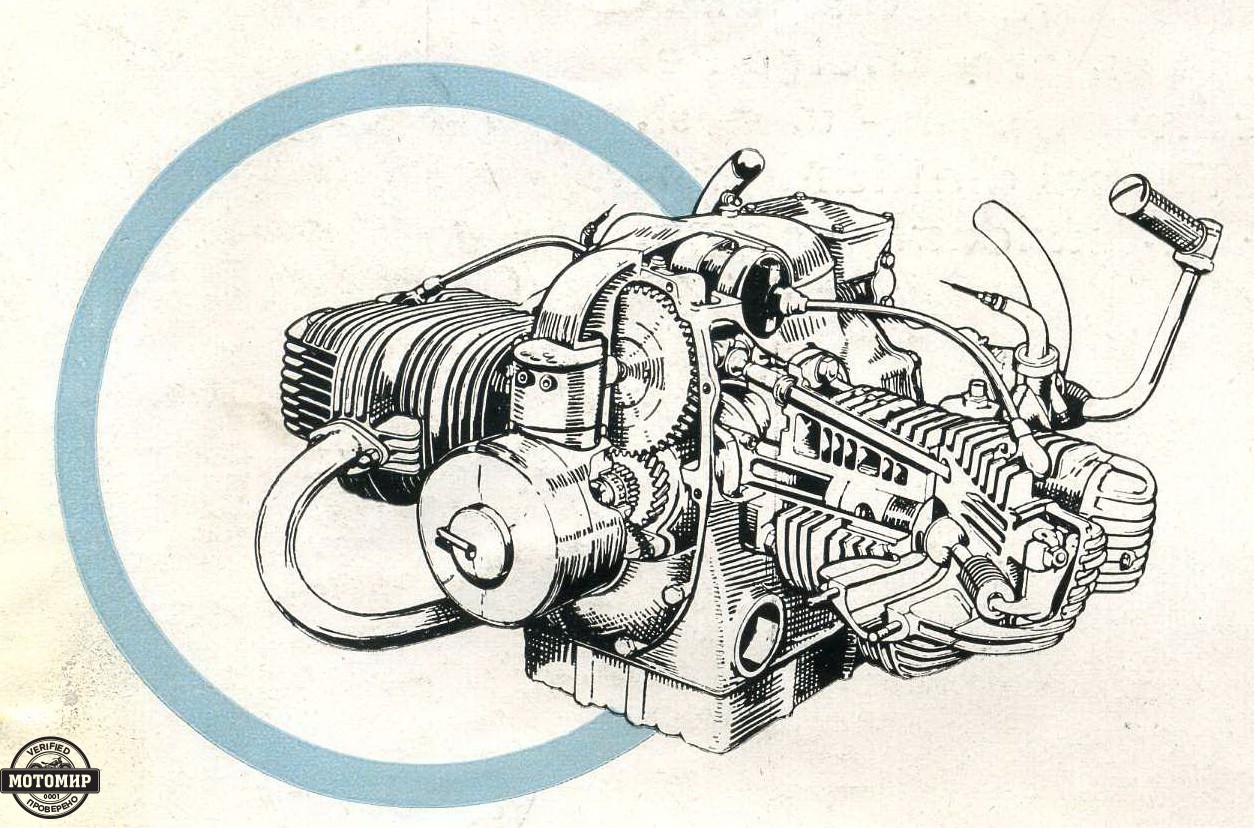
The Zündapp motorcycles, equipped with flat engines, are often compared to BMW motorcycles due to the fact that both have a similarity of appearance. But if we look closer, we’ll see that they’re completely different. The crankshaft of the Zündapp KS600 rotated on three main bearings (two roller bearings and one plain bearing). Rods were set on the crankshaft on roller bearings with bearing cages. The camshaft was installed in the crankcase top half and was driven by gears made of Novotext. These gears were more fragile but produced less noise. Besides, Novotext was able to be well oiled. Kickstarter had a bevel gearing, so the engine could be started more easily compared to BMW. Double-disk clutch operated in oil mist. A four-speed gearbox was somewhat exotic: it had chain drives instead of pinion drives for the purpose of smooth and silent operation. The gear shift was both hand and foot-operated. Rear-wheel drive was implemented via a drive shaft with two couplings.
The frame made of pressed elements was heavy and strong. The rear suspension was rigid. The machine had a parallelogram fork.
The Zündapp KS600 was a pre-model for a special military motorcycle KS750, manufacturing of which had started in 1941. However, the production of KS600 machines didn’t stop, they were still used as mobile generating sets.
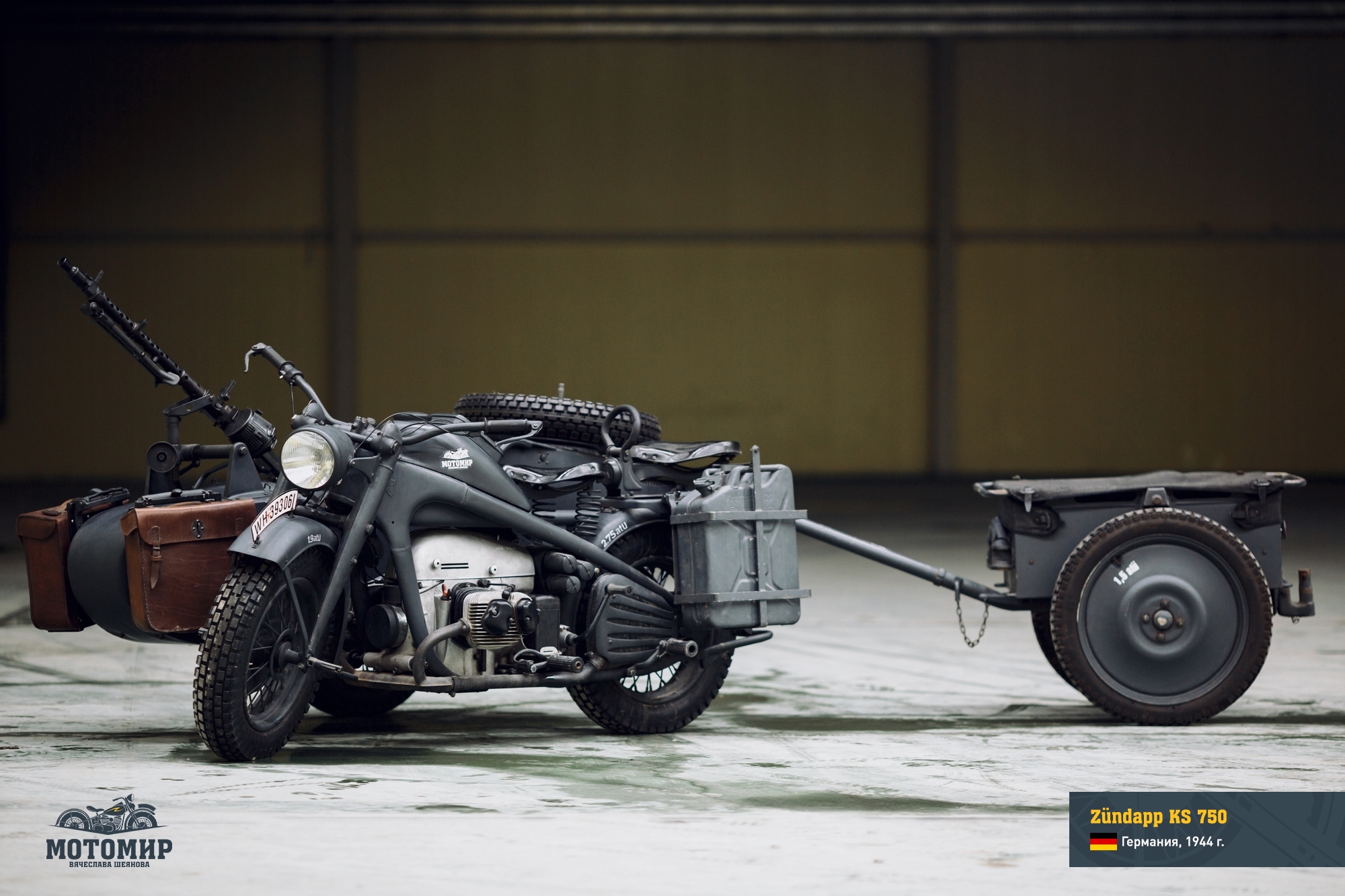

Zundapp KS750 from the «Motorworld by V.Sheynov» collection
In the early postwar years, Germany was prohibited to manufacture motorcycles equipped with engines, which had a displacement of more than 250 cc. In 1949, the ban was lifted and the Germany restarted the manufacturing of Zündapp KS600 in Nurenberg. The designing of a successor had started right after that. Zündapp KS601, a new model, was introduced in 1950. The KS601 got a significantly upgraded powertrain, based on the KS600 model, and a brand new chassis.
| Manufacturer | Zündapp Werke, GmbH, Nuremberg (Germany) |
| Years of manufacture | 1938 – 1941, 1949-1951 |
| Quantity produced, units | 21 499 |
| Price | 1395 RM |
| Today’s value | N/A |
| ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION | |
| Type | Flat-twin, 4-stroke |
| Engine capacity, cc | 597 |
| Bore and stroke, mm | 75 х 67,6 |
| Engine rating | 28 hp at 4800 rpm |
| Sparking | Magdino Noris |
| Carburetor | Amal M76 |
| Battery | 6 V |
| Clutch | Double plate in oil-bath |
| Transmission | 4-speed |
| FRAME AND WHEELBASE | |
| Frame type | Stamped steel duplex |
| Front suspension | Parallelogram, with hydraulic shock absorber |
| Rear suspension | Rigid |
| Brakes | Drum type |
| Wheel size | 3,50 x 19 |
| DIMENSIONS | |
| Length, mm | 2 150 |
| Width, mm | 885 |
| Height, mm | 960 |
| Wheelbase, mm | 1390 |
| Ground clearance, mm | 125 |
| Seat height, mm | 720 |
| Mass, kg | 195 |
| Gas tank size, l | 15 |
| Maximum speed, km/h | 145 |
| Range, km | N/A |